HTTP cookies (also called web cookies, Internet cookies, browser cookies, or simply cookies) are small blocks of data created by a web server while a user is browsing a website and are saved on the user’s computer or other device.
Cookies serve useful and sometimes essential functions on the web. They enable web servers to store stateful information (such as attestation information) or to track the user’s browsing activity (including clicking particular buttons, logging in, or recording which pages were visited in the past).
Authentication cookies are commonly used by web servers to authenticate that a user is logged in, and with which account they are logged in. Without the cookie, users would need to authenticate themselves by logging in on each page containing sensitive information that they wish to access. The security of an authentication cookie generally depends on the security of the issuing website and the user’s web browser, and on whether the cookie data is encrypted. Security vulnerabilities may allow a cookie’s data to be read by an attacker, used to gain access to user data, or used to gain access (with the user’s credentials) to the website to which the cookie belongs.
For security and privacy reasons, users are therefore prompted with a cookie acceptance policy banner that they must actively consent to before they may enter a site.
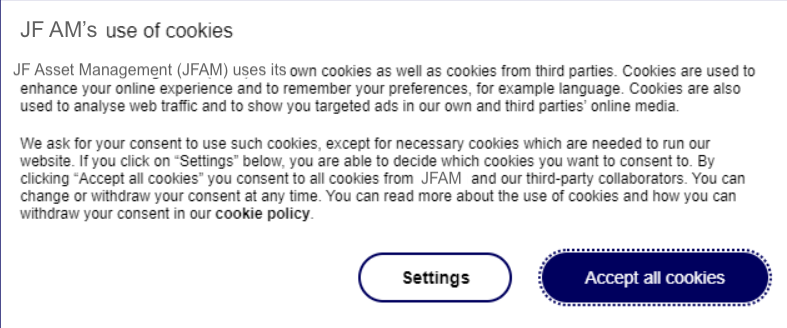
Consent
The user’s consent is saved in a cookie called `wscrCookieConsent` – this has various values associated with it dependent on the level of consent given.
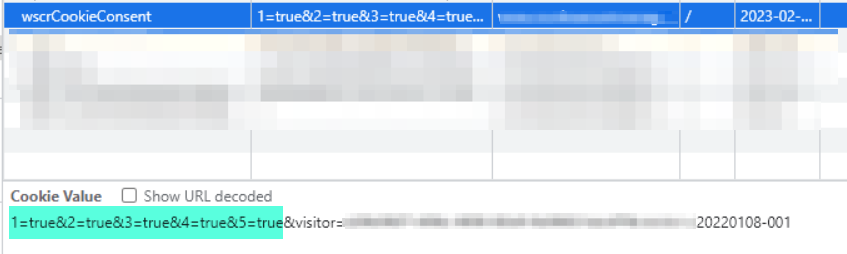
The numbers 1 to 5 correspond to cookie categories:
- 1 = Necessary cookies
- 3 = Analytics cookies
- 4 = Marketing cookies
The boolean value “true/false” indicates if the visitor has accepted (true) or rejected (false) the cookies in that category.
